Table of Contents
- Definition
- Computer language
- History of microprocessor
 |
| microprocessor-chip |
The microprocessor is a Programmable integrating device having computing, storing, retrieving and decision-making capabilities.
- A computer with a microprocessor as its CPU is known as a microcomputer.
- A microcomputer on a single chip is known as a microcontroller.
- Mnemonic-- A combination of letters to suggest the operation of an instruction.
- Program-- Effect of instruction written in a specific sequence for the computer to accomplish a given task.
- Machine language-- A set of instructions executed directly by the computer's CPU.
- Assembly language-- It is low-level programming there is a strong correspondence between the language and architectures' machine code instructions.
- Low-level language-- Machine-specific languages are known as low-level language examples- machine language, assembly language.
- High-level language-- A programming language that enables a programmer to write programs that are independent of a particular type of computer.
- Assembler-- It is a computer program that translates an assembly language program for Mnemonics to the binary machine code of a computer.
- Compiler-- A program that translates high-level language program into machine level language by translating the entire program at a time and educating it.
- Interpreter-- Translate high-level language program in object codes statement wise.
High-level language programming is required for translators like a compiler or an interpreter to translate the program written in a high-level language to binary form.
- Bit-- A binary digit, 0 0r 1.
- Nibble-- A group of four (4) bits.
- Byte-- A group of eight (8) bits.
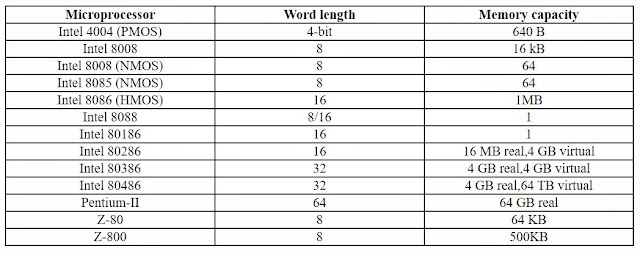
- Word-- A group of the byte the computer recognizes and processors at a time.
ALSO, READ Evolution of Microprocessors





0 Comments